Ampoule Filling Lines
In the pharmaceutical industry, an ampoule is a small, airtight glass container designed to maintain the sterility and integrity of its contents. Commonly used for storing injectable medications, vaccines, and sensitive liquids or gases, ampoules protect against air, moisture, and contaminants. They are sealed to ensure product stability until the moment of use. Ampoules come in two main types: open ampoules, which are ready for filling and sealing, and closed ampoules, which require an opening step before filling. Their use is critical in ensuring safe and contamination-free drug delivery.
Filling Line Comes Under Different contentment system
LAF – Laminar Air Flow
A steady flow of clean, filtered air (through HEPA filters) keeps dust and particles away from the filling and sealing area. The whole setup needs to run in a very clean space—Grade B or better
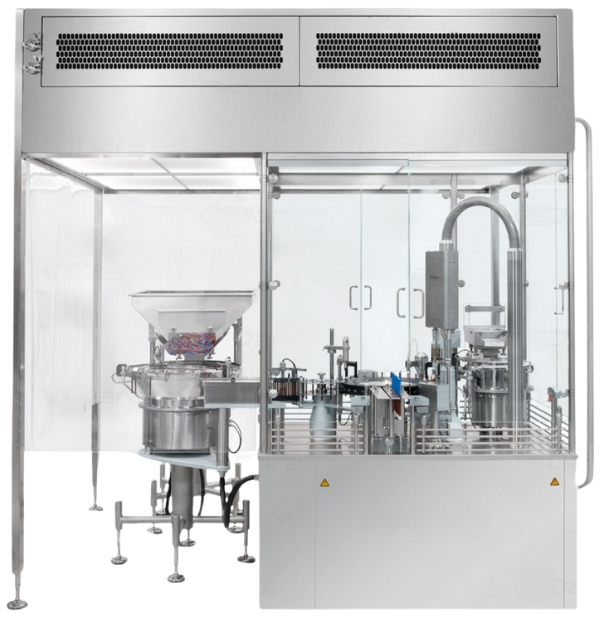


ORABS – Open Restricted Access Barrier System
A glass cabinet with gloves and ports keeps the operator separate from the product, while filtered air (LAF) adds extra protection. Air comes from and returns to the same room. The line must run in a cleanroom of Grade B or higher.
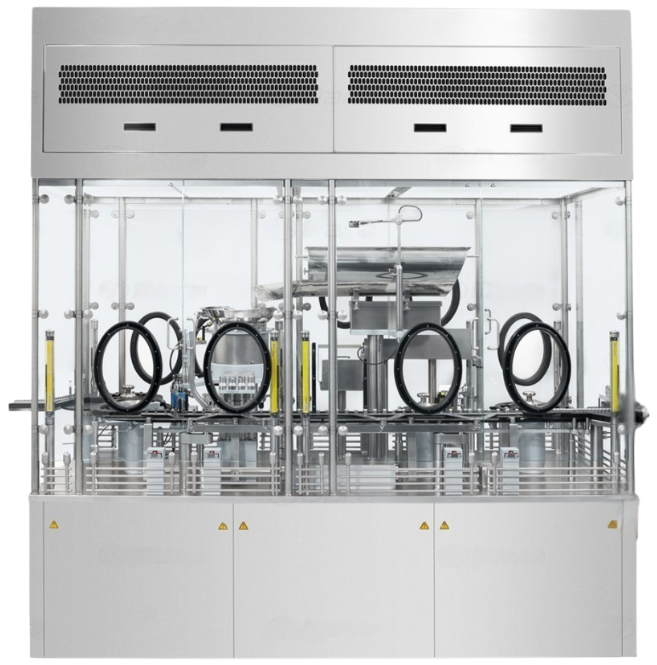
CRABS – Closed Restricted Access Barrier System
A sealed barrier keeps the operator and product fully separated. Air is recirculated in a closed system with controlled pressure, temperature, and humidity. The setup runs in a Grade B or higher cleanroom.
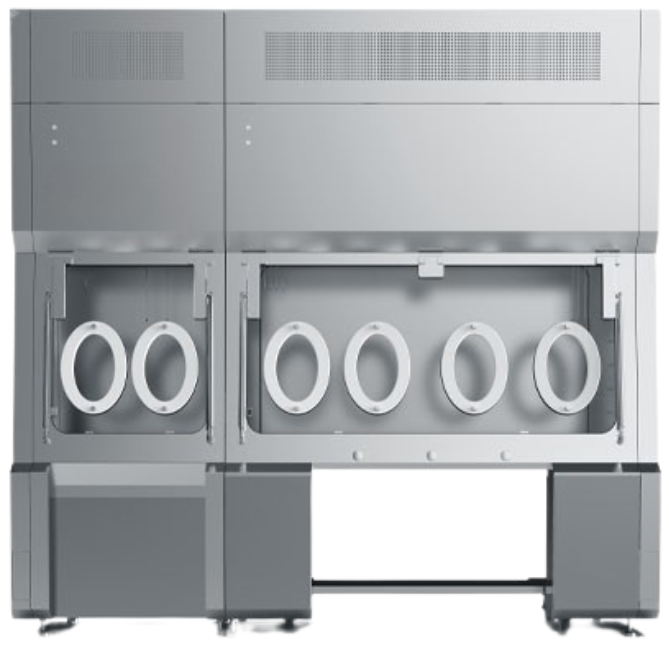
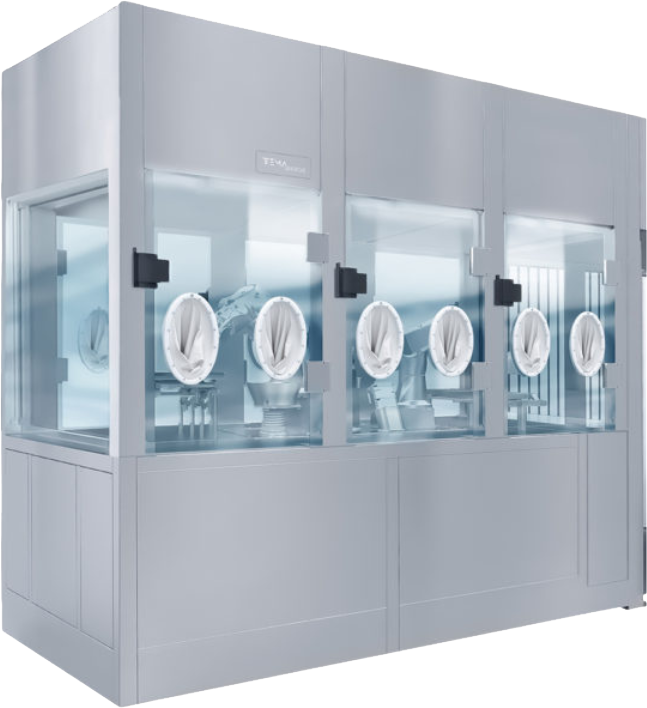


ISOLATOR
Highest level of safety for handling sterile or toxic products. It includes a sealed chamber, transfer ports, and set procedures. With built-in decontamination (VHP), sterility checks, and particle monitoring, it can safely run even in an ISO 8 or Grade D room.
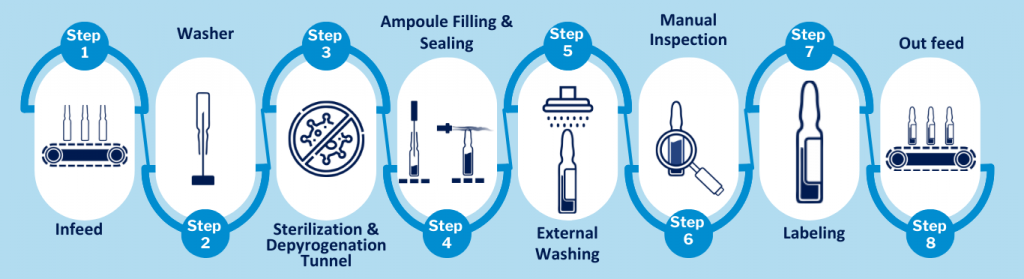
- Ampoule Rotary Washing Machine
- Sterilisation & Depyrogenation Tunnel
- Ampoule Filling Line
- Sealing Mechanism
- Rotary Sticker Labelling Machine
The ampoule washing machine plays a crucial role at the beginning of the filling line by thoroughly cleaning each ampoule to ensure it is free from particles and contaminants. The machine performs a 6-step washing and rinsing process, which includes:
|
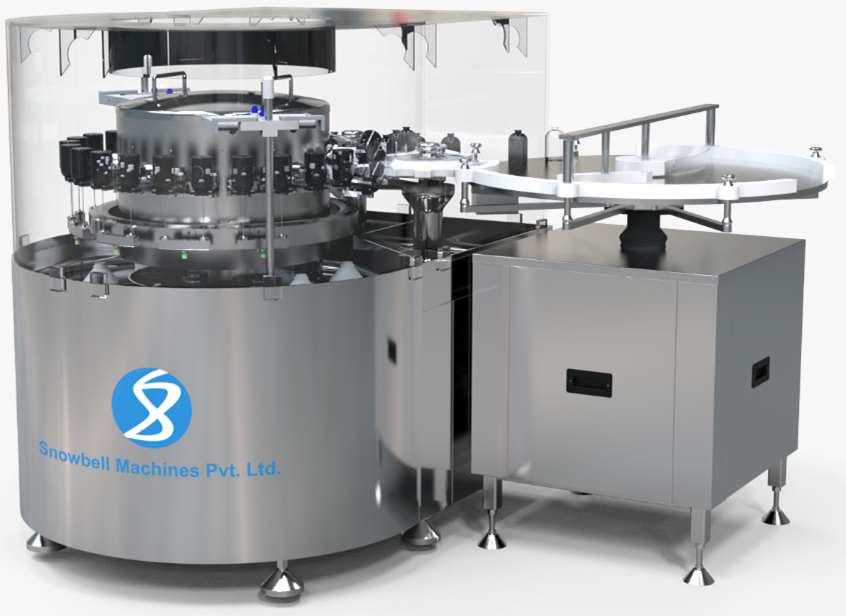 |
Optional Features Based on Customer Requirements:
- Ultrasonic Washing: For enhanced cleaning, particularly in applications requiring ultra-high sterility, an ultrasonic washing unit can be added. This technology uses high-frequency sound waves in a liquid medium to dislodge and remove microscopic particles.
- Siliconization (Optional): In some applications, siliconization may be required to improve the internal surface smoothness of ampoules. A fine mist of pharmaceutical-grade silicone is sprayed inside the ampoule.
- After washing, the Ampoule pass through this tunnel for sterilization and depyrogenation. This tunnel is divided into three parts, Dry Zone, Hot Zone and Cool Zone
- Drying zone: The ampoules are dried to remove the residual water left inside the ampoules.
- Heating zone (sterilization): The ampoules are sterilized & depyrogenated by heating them to a temperature greater than 300 °C.
- Cooling Zone: This is where the temperature of ampoules is brought down to room temperature.
The core of the process is where the cleaned, sterilized, and depyrogenated Ampoules are filled with the liquid product. The process begins with ampoules being fed through a conveyor belt to the filling and sealing machine.
The ampoule filling machine operates in a controlled environment, either within an Orabs (Open Restricted Access Barrier System) or Crabs (Closed Restricted Access Barrier System). A precise pump fills each ampoule with the correct liquid amount, while nitrogen injection before and after filling protects the product.
Filled ampoules are sealed at the sealing station by melting the glass tip to create an airtight seal. The sealing station has burners that preheat the ampoule tip and then seal it. Mixing oxygen and LPG gas generates flames for sealing.
Once filled and sealed, the ampoules are passed through a rotary sticker labelling machine. This machine applies labels with essential product information such as dosage, batch numbers, expiry dates, and barcodes for traceability and regulatory compliance.
Product Flow